Chapter 6 Analysis by Methods
Bar charts and tables to examine how contributions to conferences vary by methods
#spec(cpdata)
metdata <- cpdata %>%
select_if(is.numeric) %>%
gather(key = Method, value = count, Empirical:`Remote sensing`) %>%
filter(count > 0) %>%
group_by(`Method`) %>%
summarise_all(sum, na.rm=T) 6.1 Total Conference Contributions
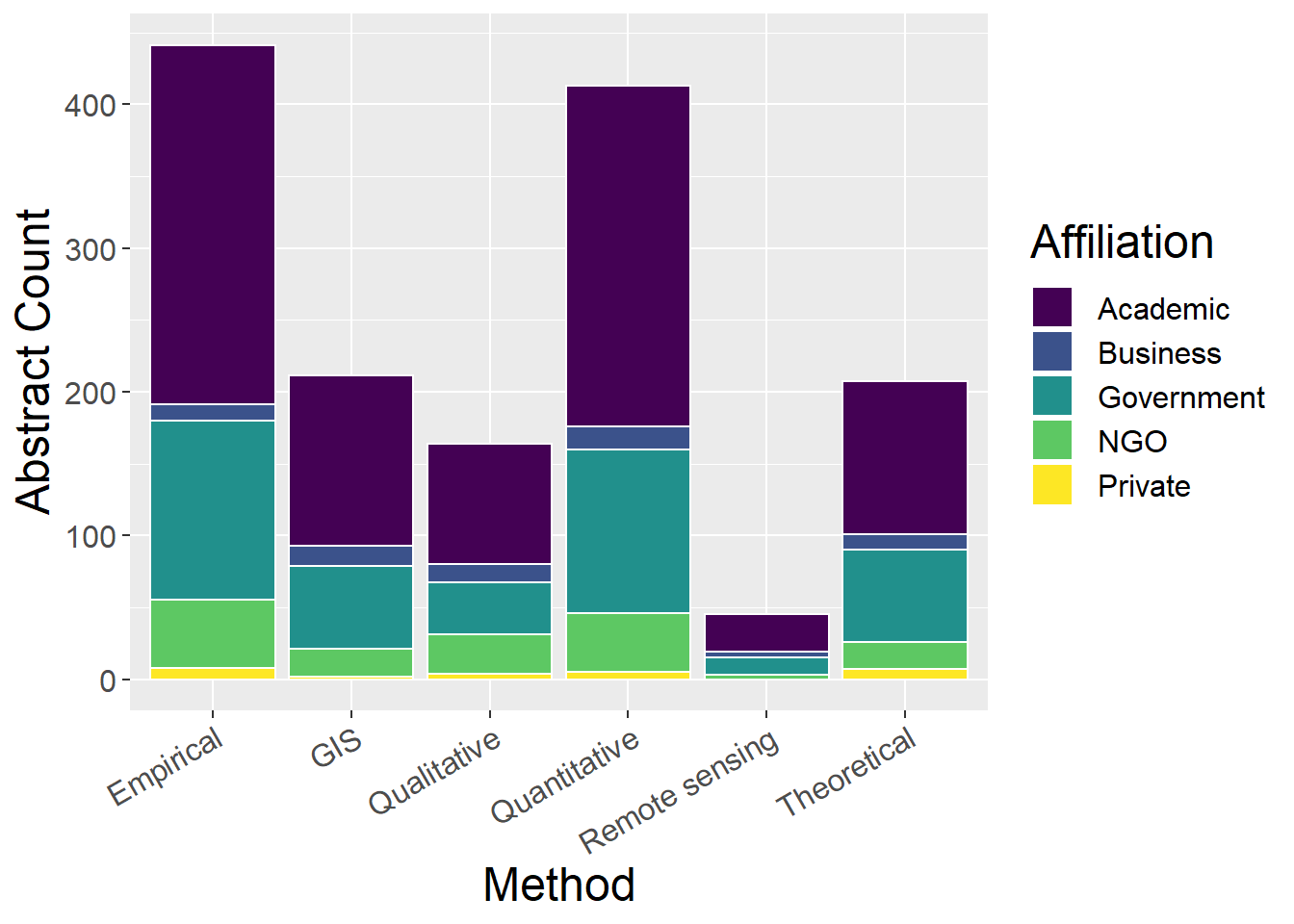
General observations:
- Empirical and Quantitative studies dominate
- little remote sensing
metdata %>%
select(Method, count) %>%
mutate(prop = count/sum(count)) %>%
mutate(prop = round(prop,3)) %>%
kable() %>%
kable_styling() %>%
scroll_box(width = "100%")| Method | count | prop |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical | 375 | 0.292 |
| GIS | 185 | 0.144 |
| Qualitative | 154 | 0.120 |
| Quantitative | 351 | 0.273 |
| Remote sensing | 41 | 0.032 |
| Theoretical | 178 | 0.139 |
ggplot(metdata, aes(x=Method, y=count)) +
geom_bar(stat="identity") +
geom_text(aes(x=Method, y=max(count), label = paste0(round(100*count / sum(count),1), "%"), vjust=-0.25)) + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(y = "Abstract Count")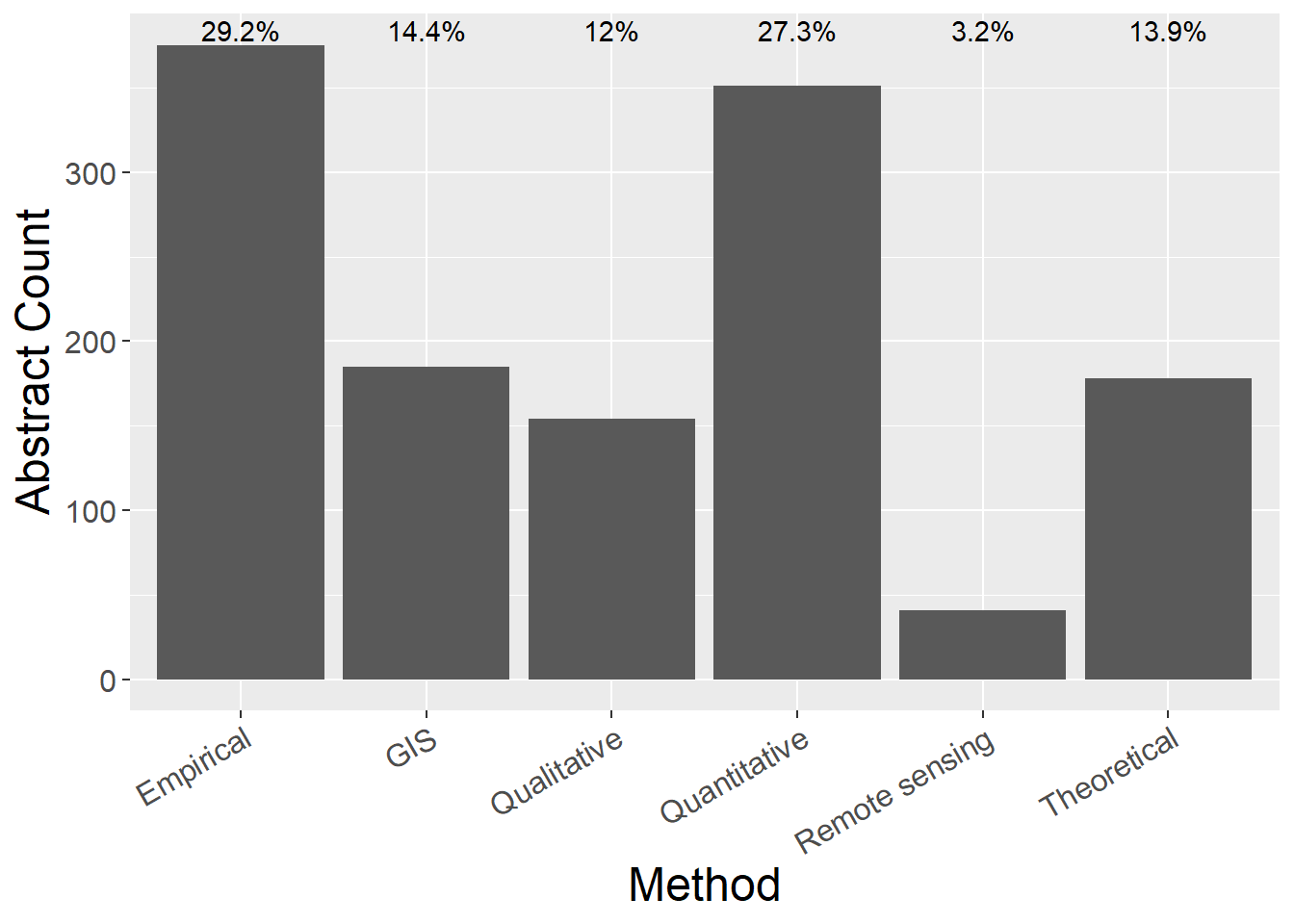
6.3 Landscape Type
6.3.1 Using all landscape types
General observations:
- Qualitative studies are most evenly distributed across landscape types
- Theoretical studies most commonly do not define a landscape type
lspCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method,`Upland rural`, `Lowland rural`, Urban, Riverscape, Seascape, `Undefined LspType`,Other) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:8])) %>% #calculate total for subsquent calcultation of proportion
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum) #calculate proportion
ggplot(lspCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Landscape Type", y = "Abstract Count", x="Method")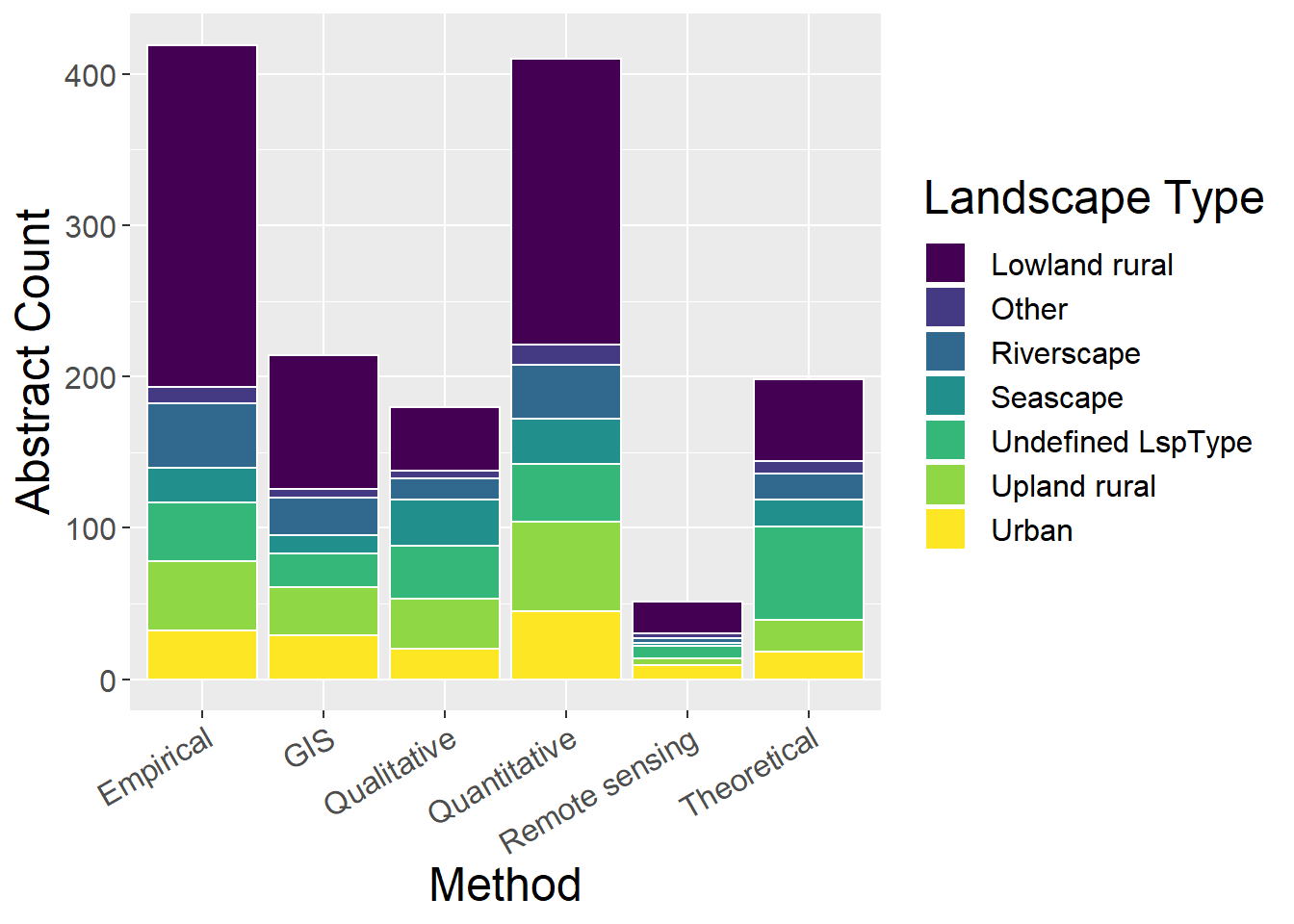
ggplot(lspCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Landscape Type", y = "Proportion", x="Method")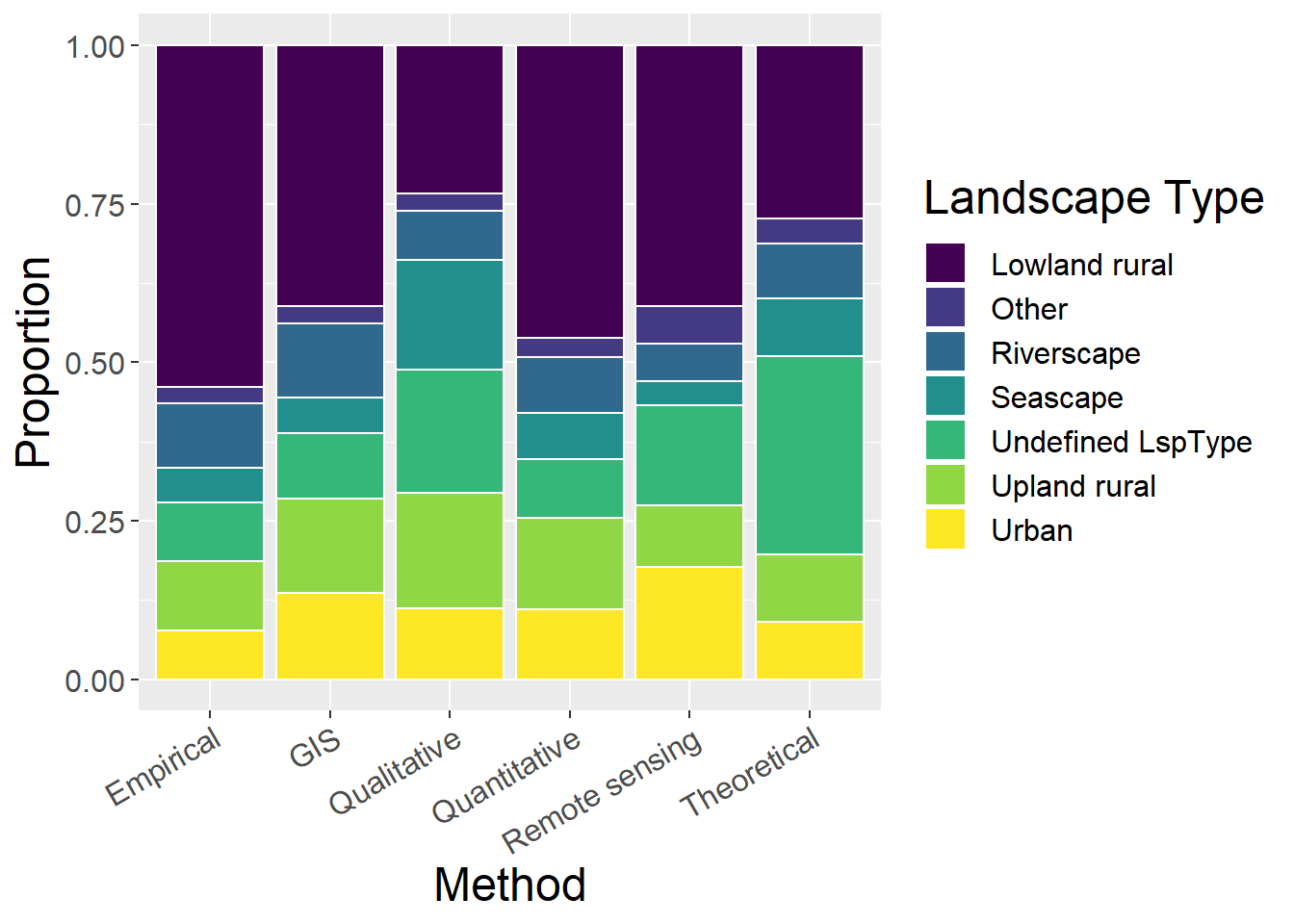
6.3.2 Without ‘Undefined LspType’ and ‘Other’ landscape types
General observations:
- This is generally less informative than with ‘un-defined’ (in contrast to other classifications)
- Does highlight that qualitative studies are most prevalent in seascape studies
lspCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method,`Upland rural`, `Lowland rural`, Urban, Riverscape, Seascape) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:6])) %>% #calculate total for subsquent calcultation of proportion
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum) #calculate proportion
ggplot(lspCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Landscape", y = "Abstract Count", x="Method")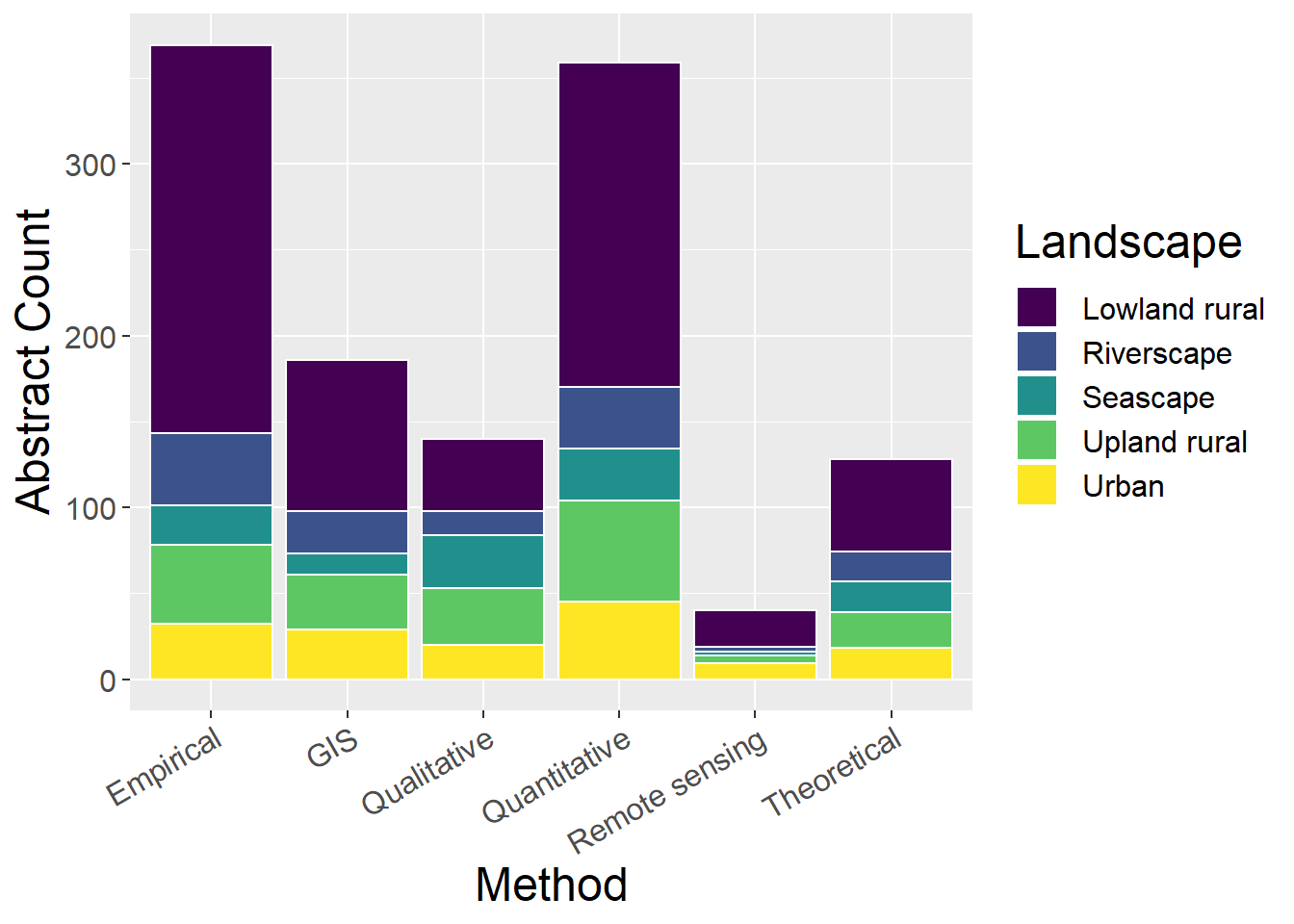
ggplot(lspCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Landscape", y = "Proportion", x="Method")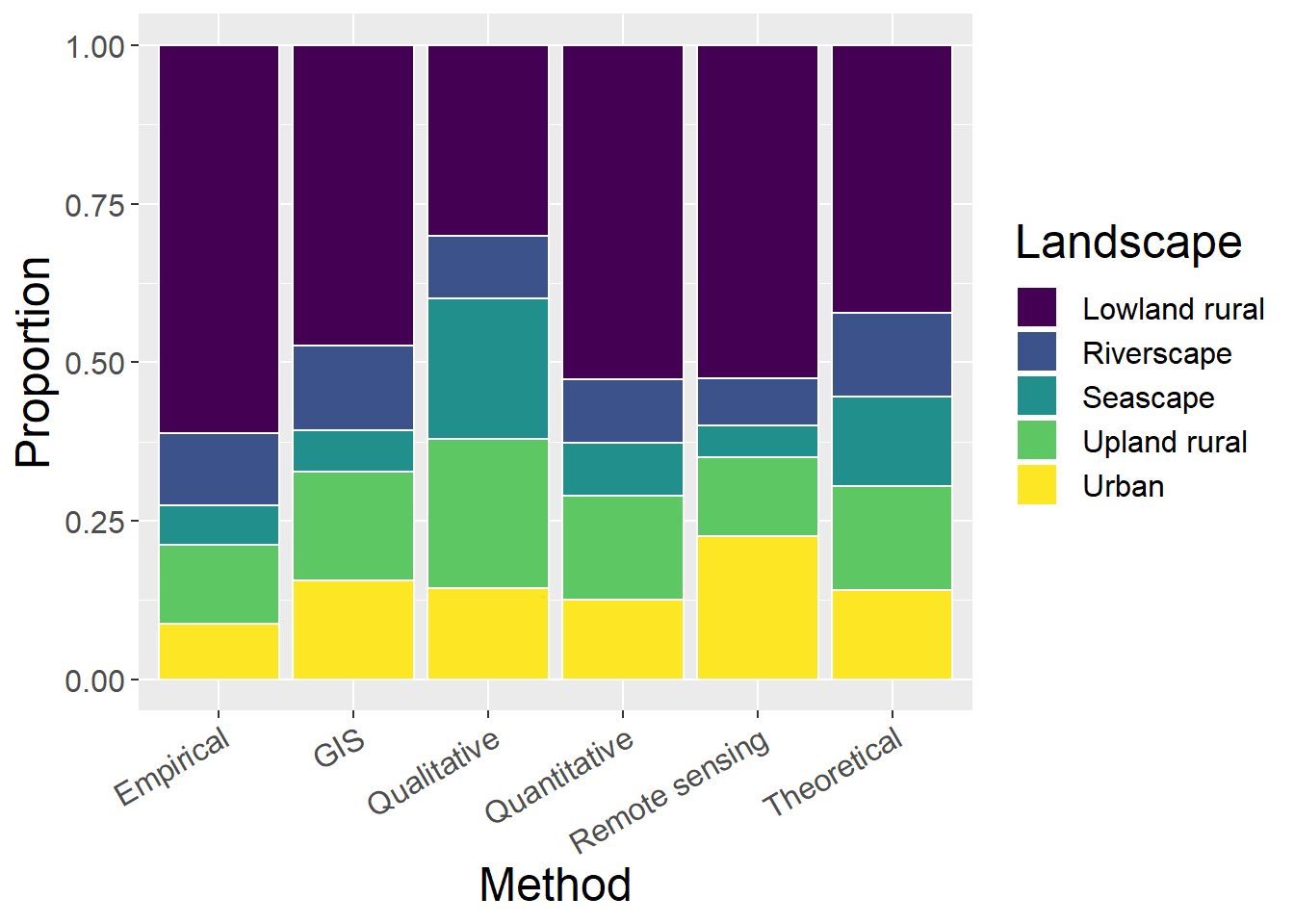
6.4 Organism
General observations
- Qualitative studies most commonly study humans
sppCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method,Mammals, Humans, Birds, Reptiles, Inverts, Plants, Amphibians, Fish, `Generic Habitat`,`Woodland Forests`) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:11])) %>% #calculate total for subsquent calcultation of proportion
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum) #calculate proportion
ggplot(sppCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Organism", y = "Abstract Type", x="Method")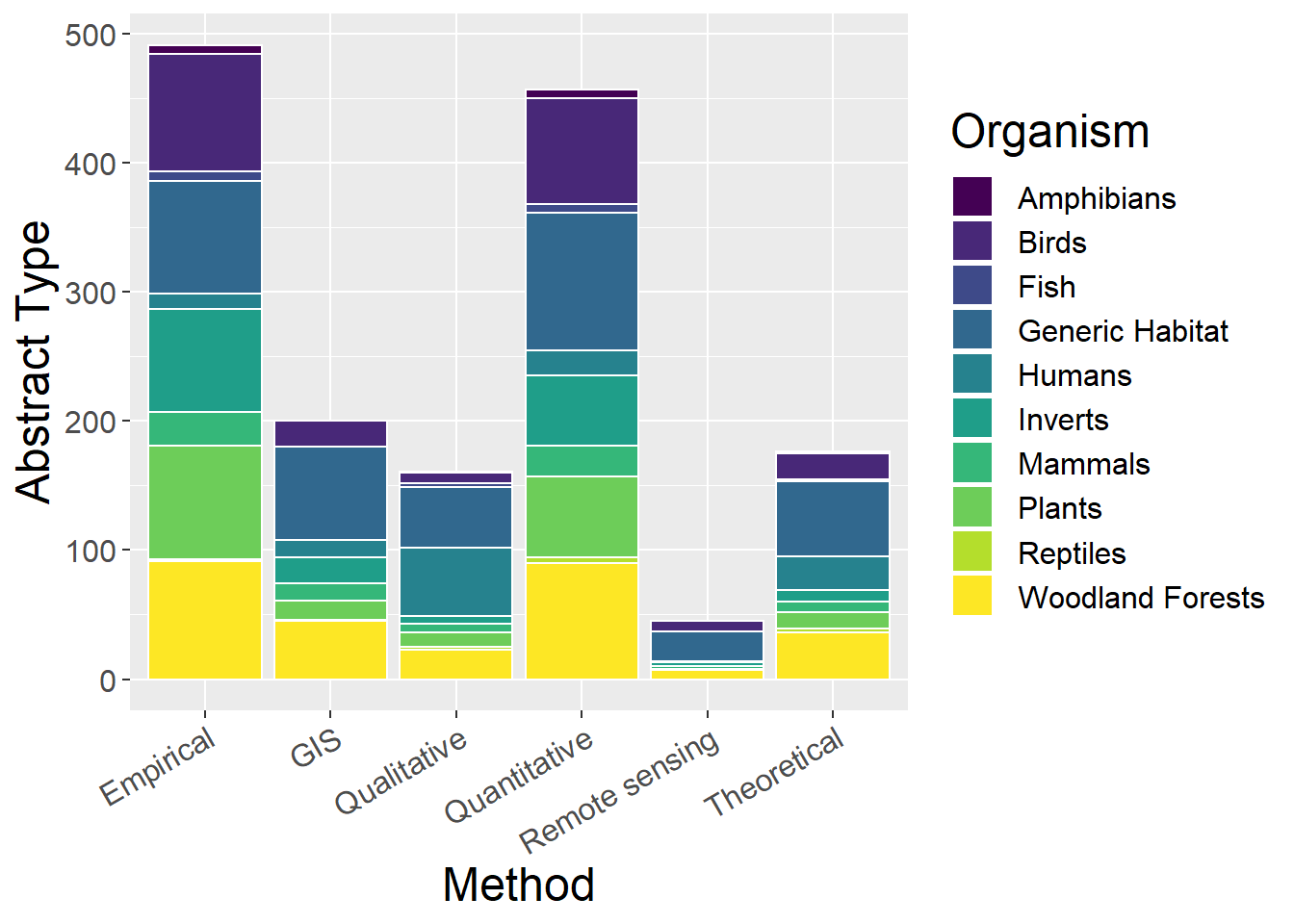
ggplot(sppCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Organism", y = "Proportion", x="Method")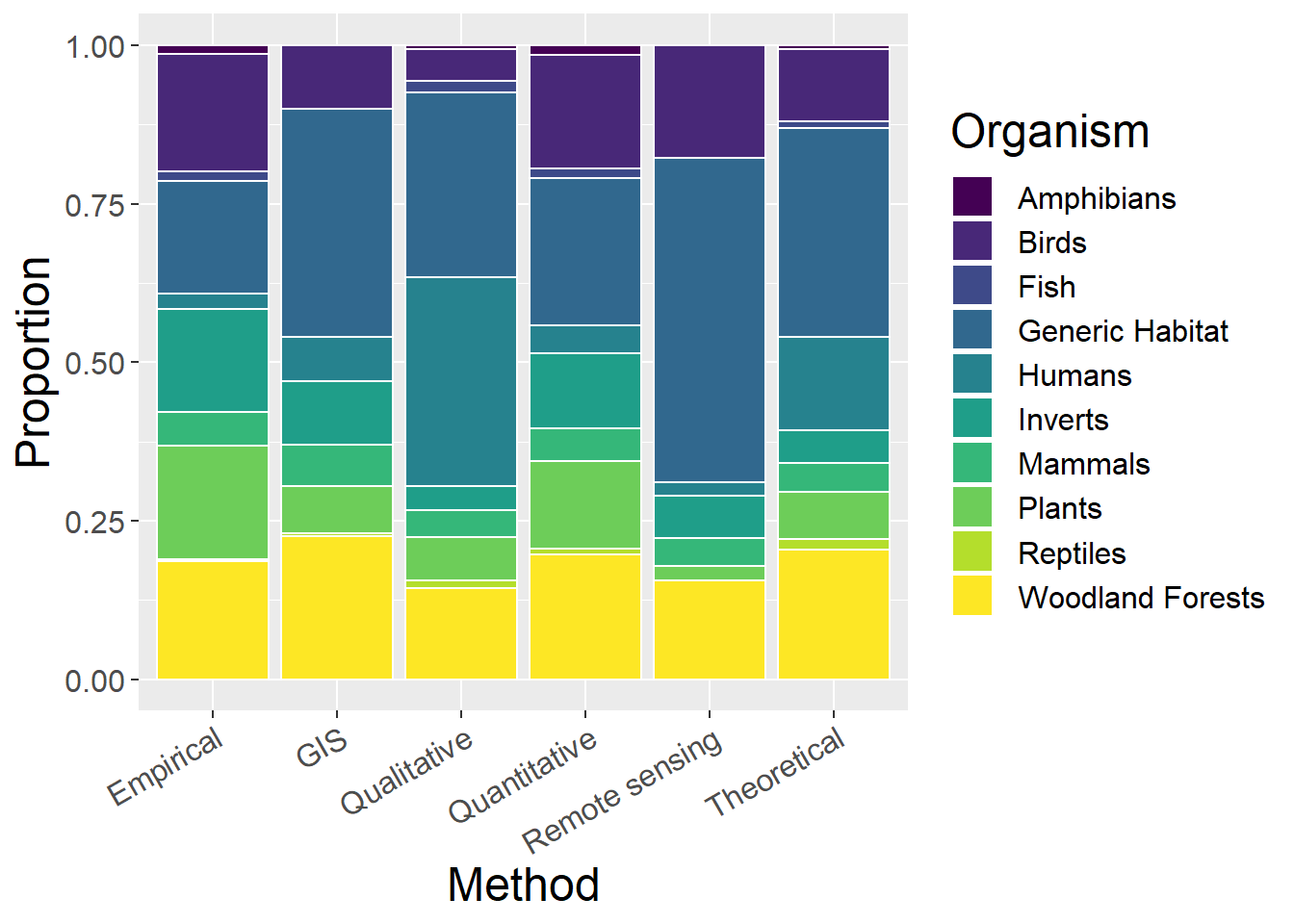
6.5 Spatial Extent
General observations:
- Theoretical studies have largely undefined extent
- No micro qualitative studies
- Very few global empirical studies, and no GIS global studies
spatialCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method, Micro, Mini, Local, Regional, National, Continental, Global,`Undefined Extent`) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:9])) %>%
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum)
factor_order <- c('Micro', 'Mini', 'Local', 'Regional', 'National', 'Continental', 'Global','Undefined Extent')
factor_labels <- c('Micro', 'Mini', 'Local', 'Regional', 'National', 'Continental', 'Global','Undefined')
ggplot(spatialCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=factor(Type, level=factor_order))) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Extent", y = "Abstract Count", x="Organism")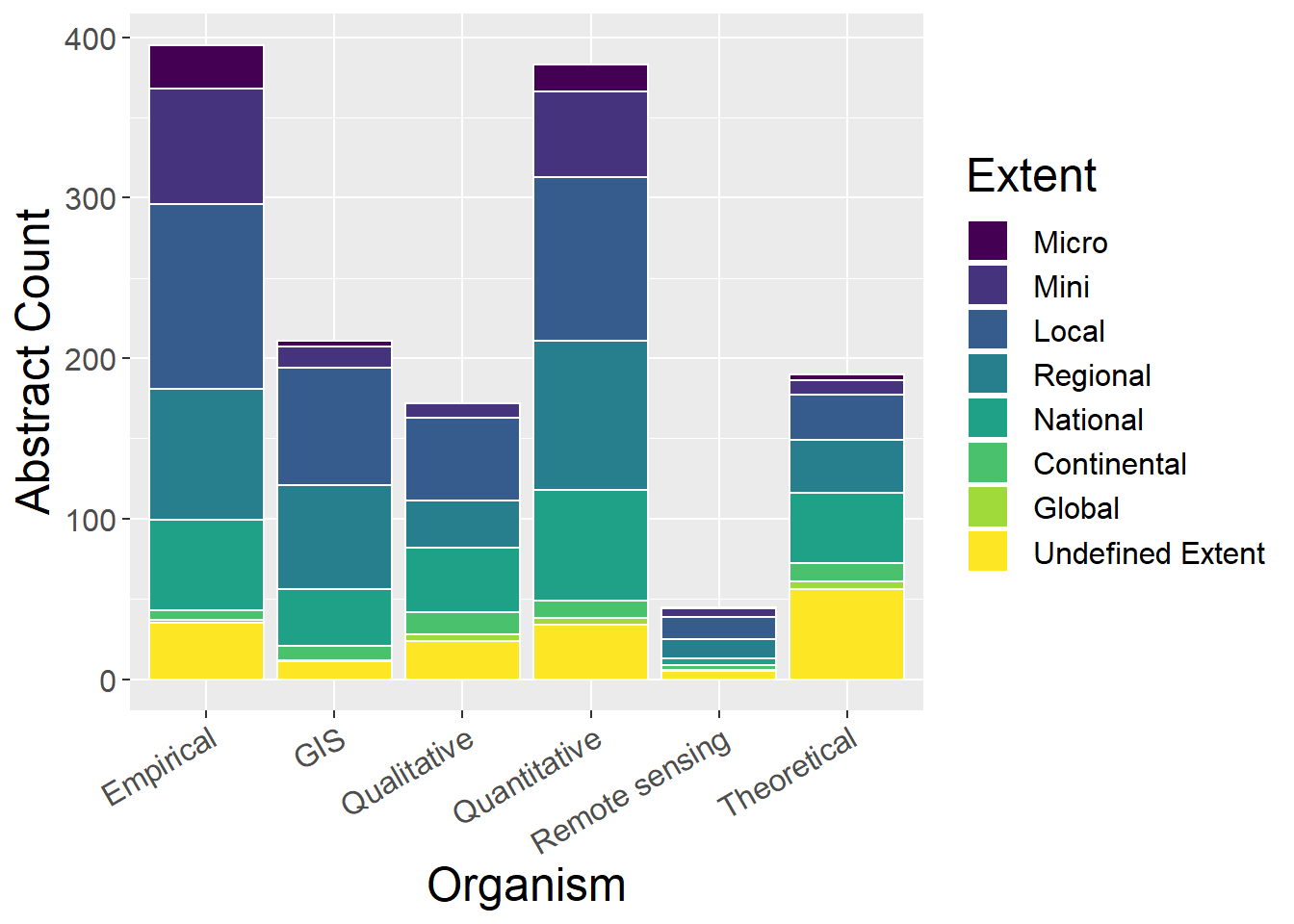
ggplot(spatialCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=factor(Type, level=factor_order))) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Extent", y = "Proportion", x="Organism")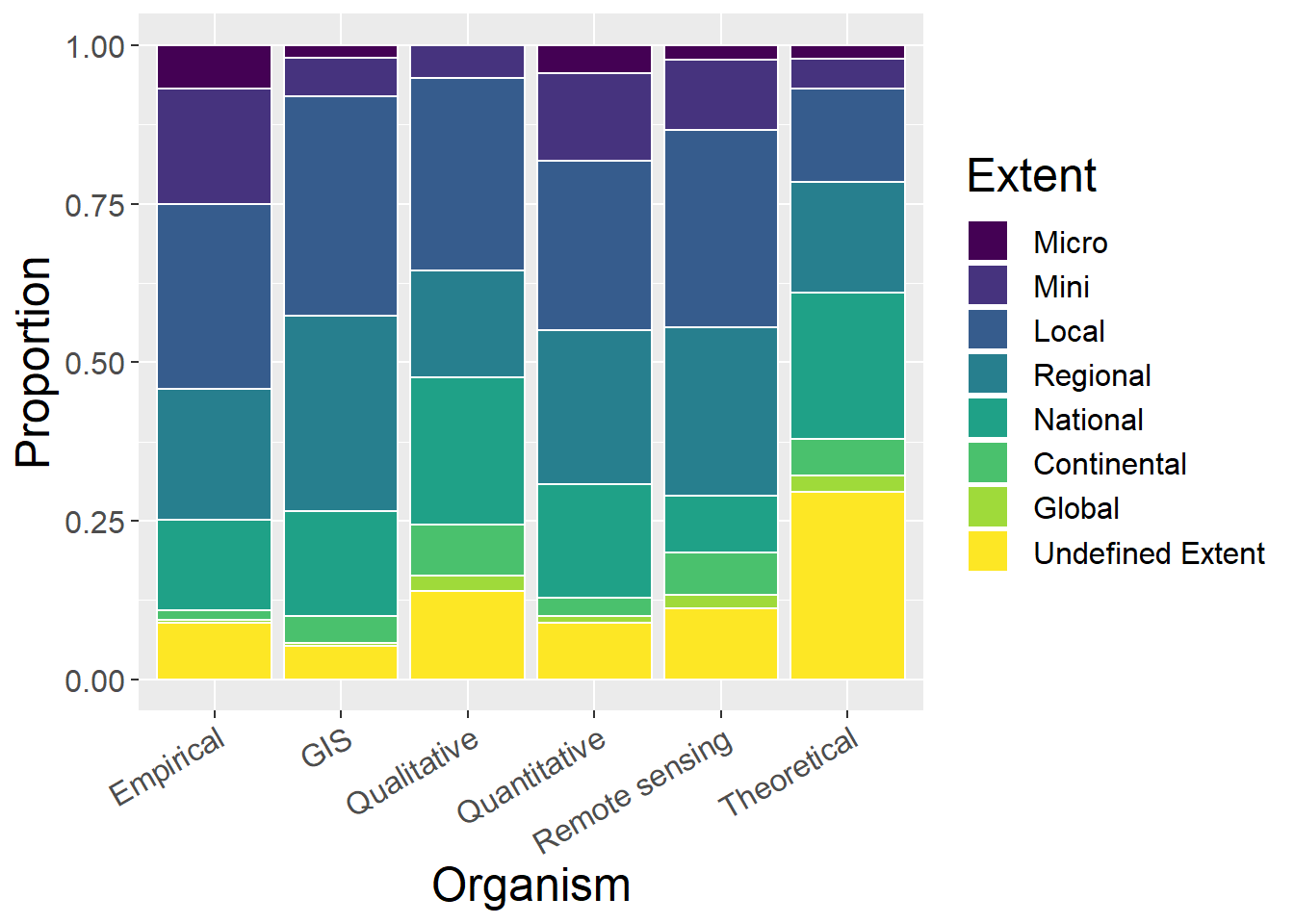
6.6 Temporal Extent
6.6.1 With undefined
General observations:
- Difficult to see much; examine without ‘undefined’
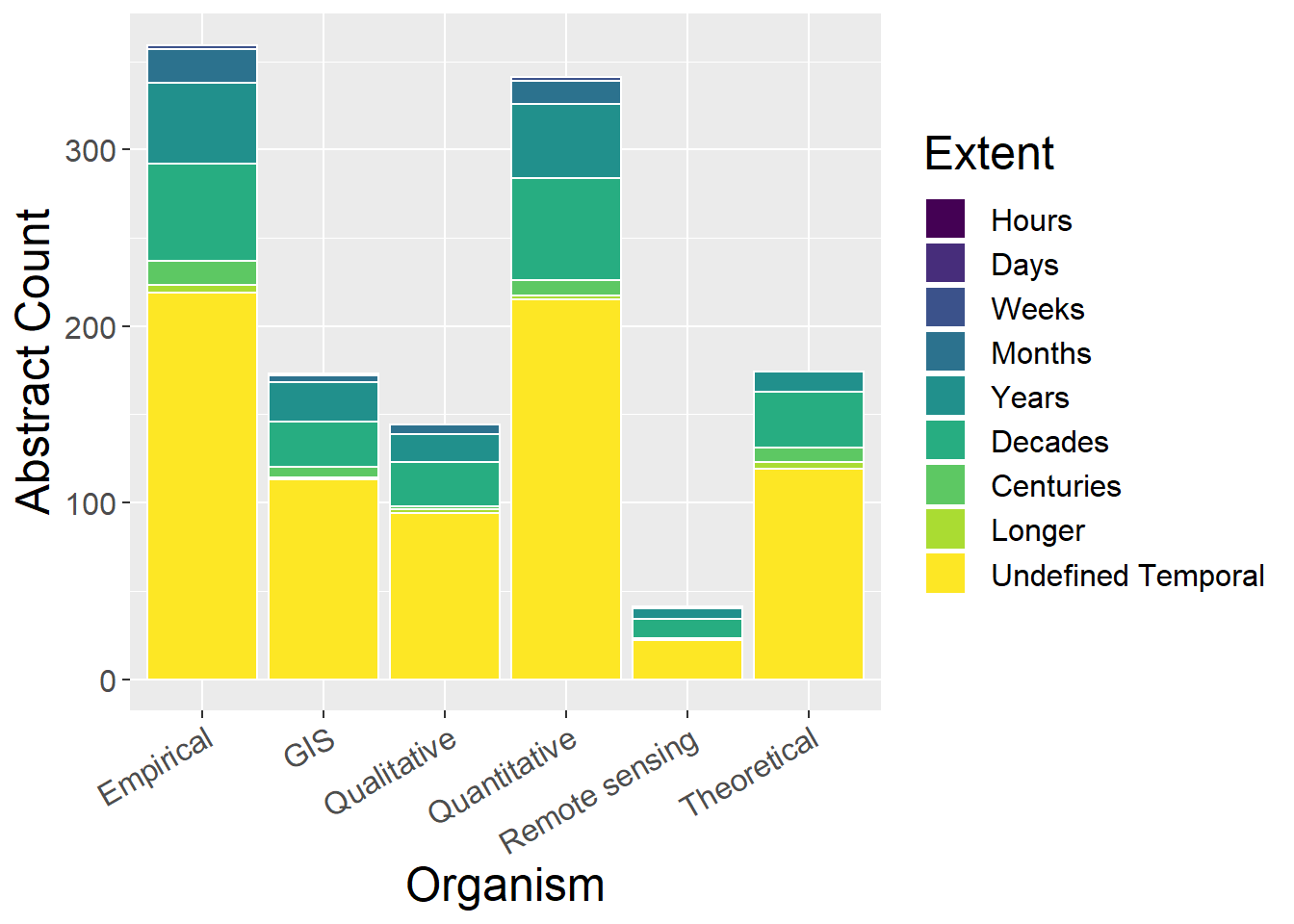
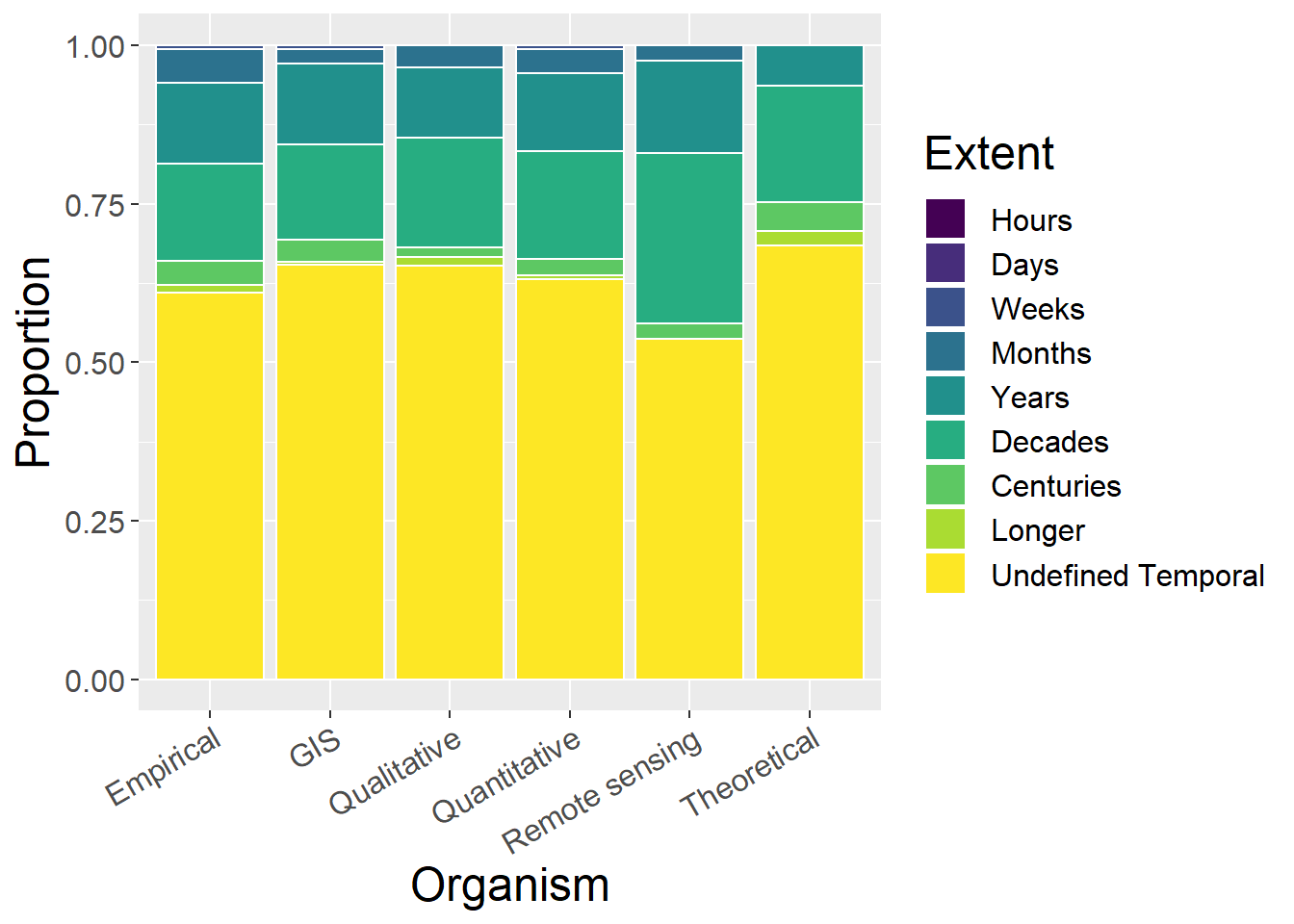
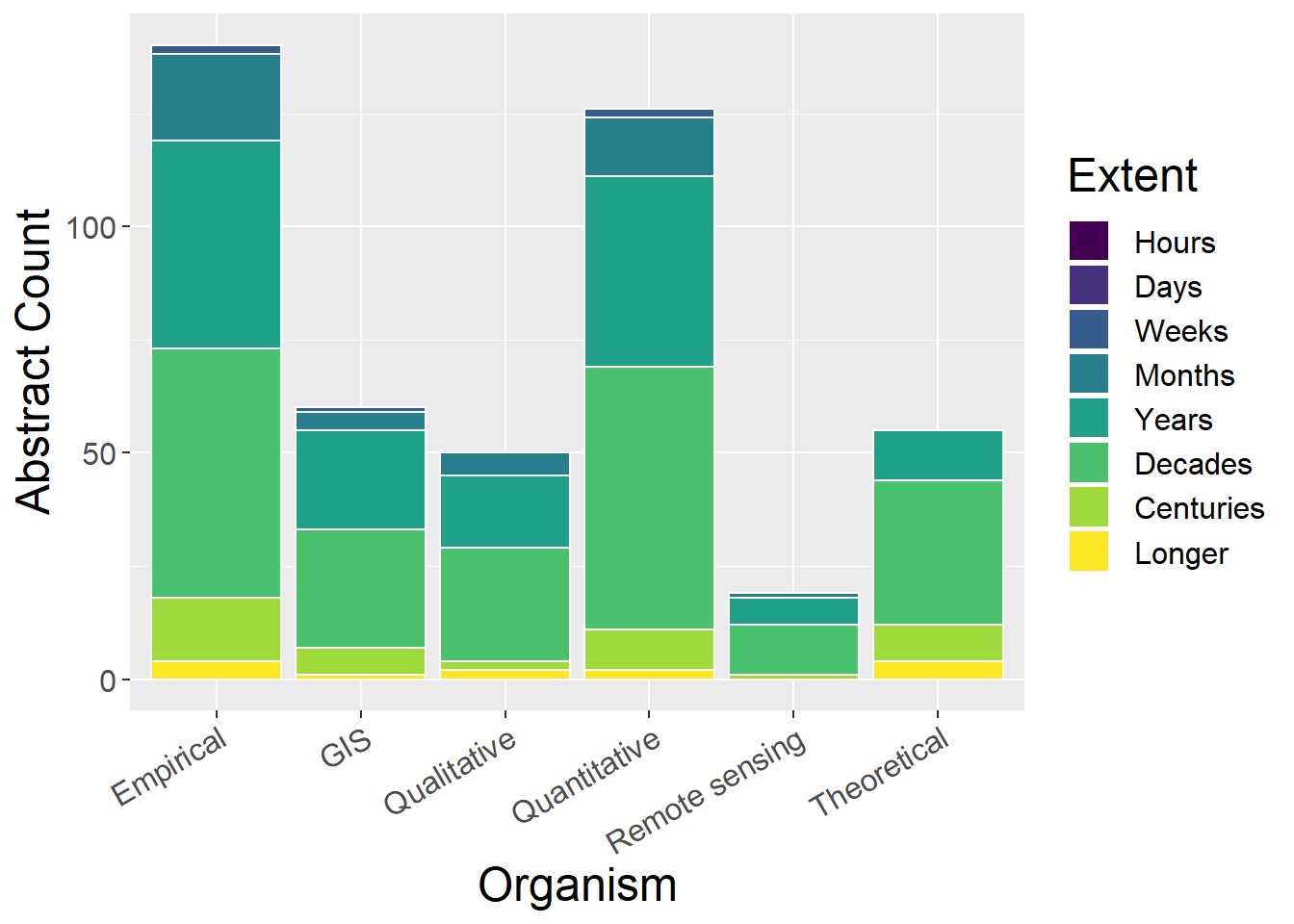
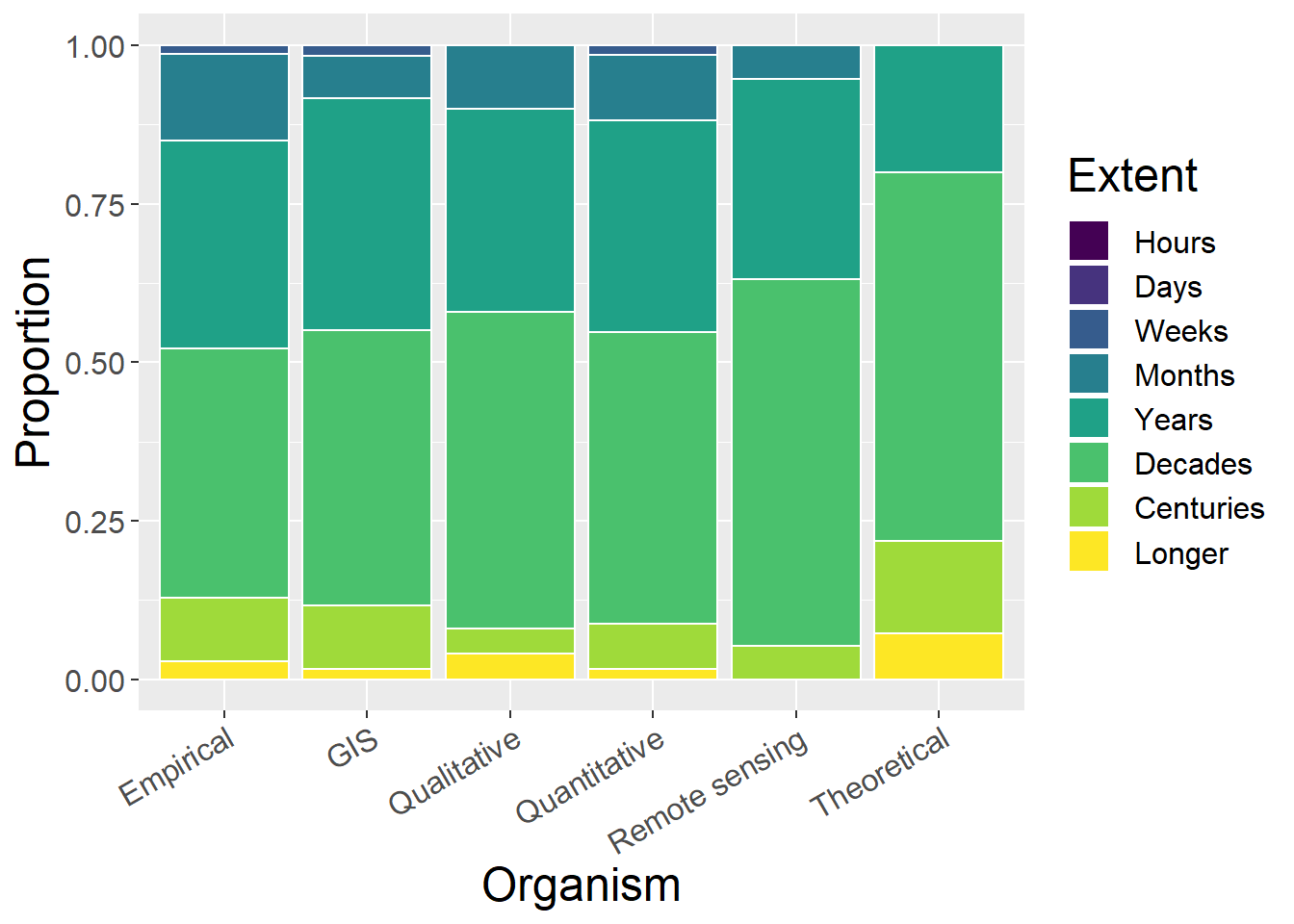
6.6.2 Without Undefined
- Theoretical studies are years or longer
- Actually, vast majority of studies are months or longer (should see this when splitting by temporal extent)
6.7 Concepts
General observations:
- Surprisingly few theoretical studies of scale and scaling?
- Relatively large number of qualitative studies are about landscape sustainability
- Relatively few empirical studies of ecosystem services
- GIS studies have largest proportion of spatial analysis and modelling (unsurprisingly)
conceptCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method, `PPS of landscapes`,
`Connectivity and fragmentation`, `Scale and scaling`,`Spatial analysis and modeling`,LUCC,`History and legacy`,`Climate change interactions`,`Ecosystem services`,`Landscape sustainability`,`Accuracy and uncertainty`
) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:11])) %>%
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum)
ggplot(conceptCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Concept", y = "Abstract Count", x="Organism")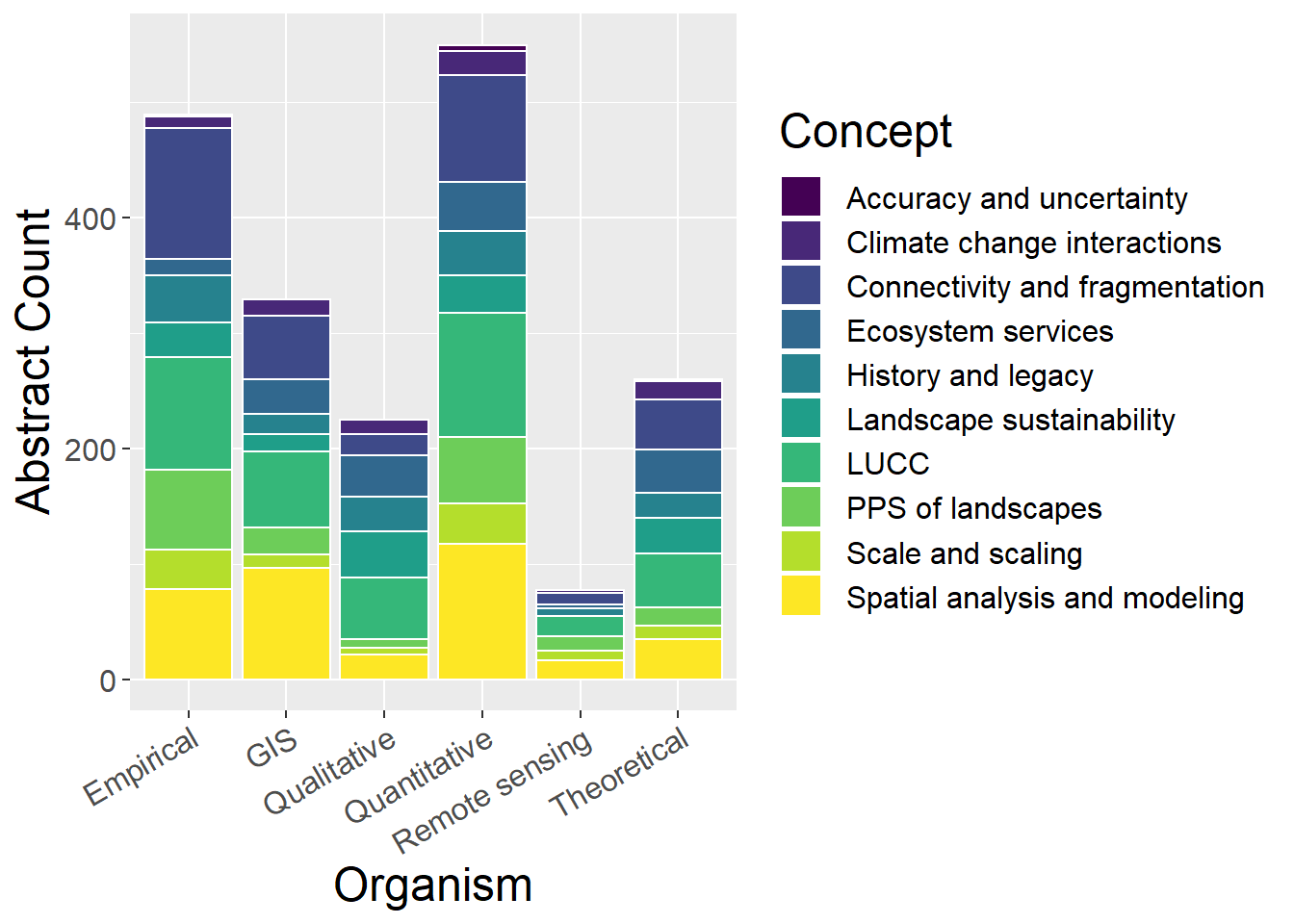
ggplot(conceptCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Concept", y = "Proportion", x="Organism")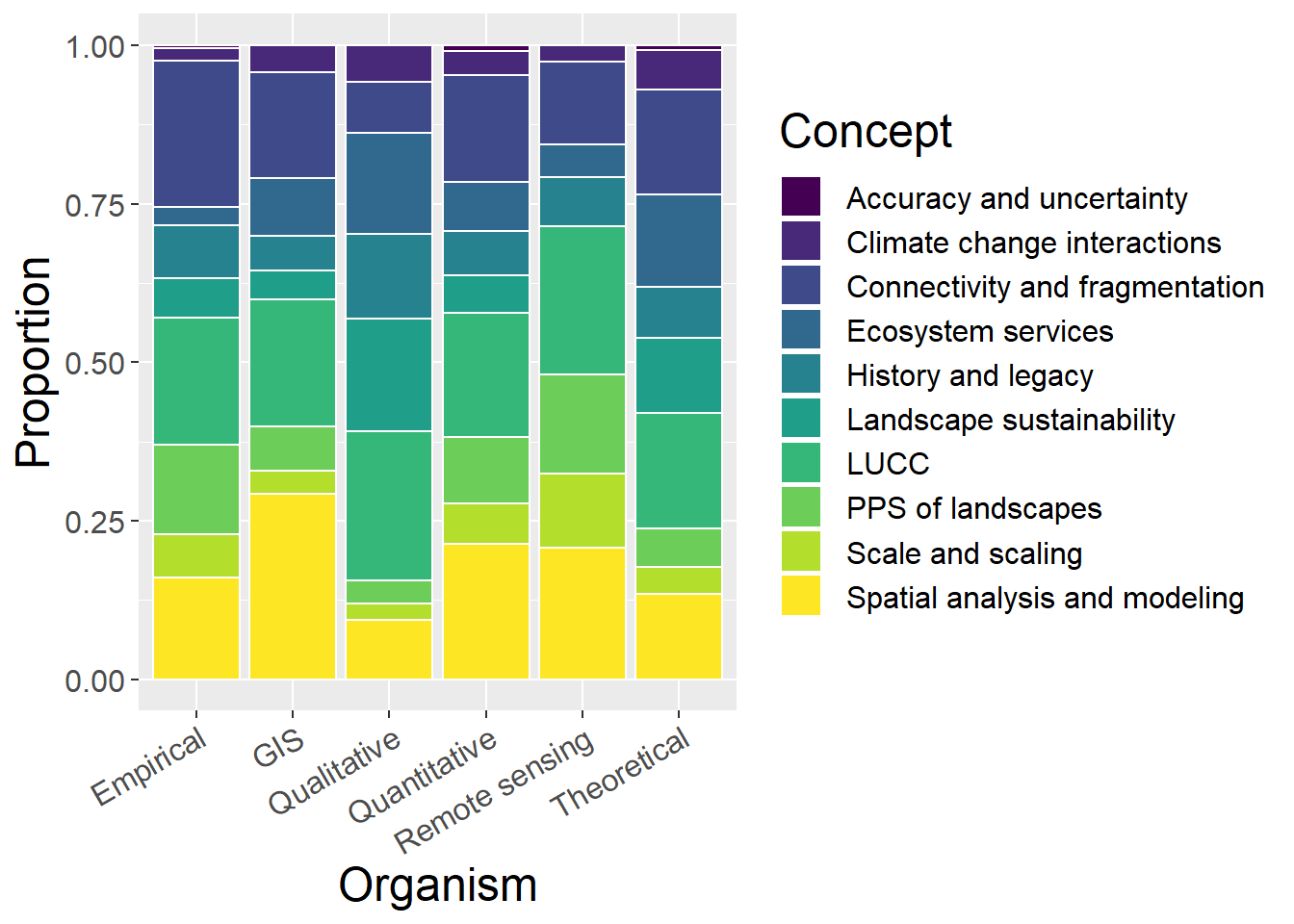
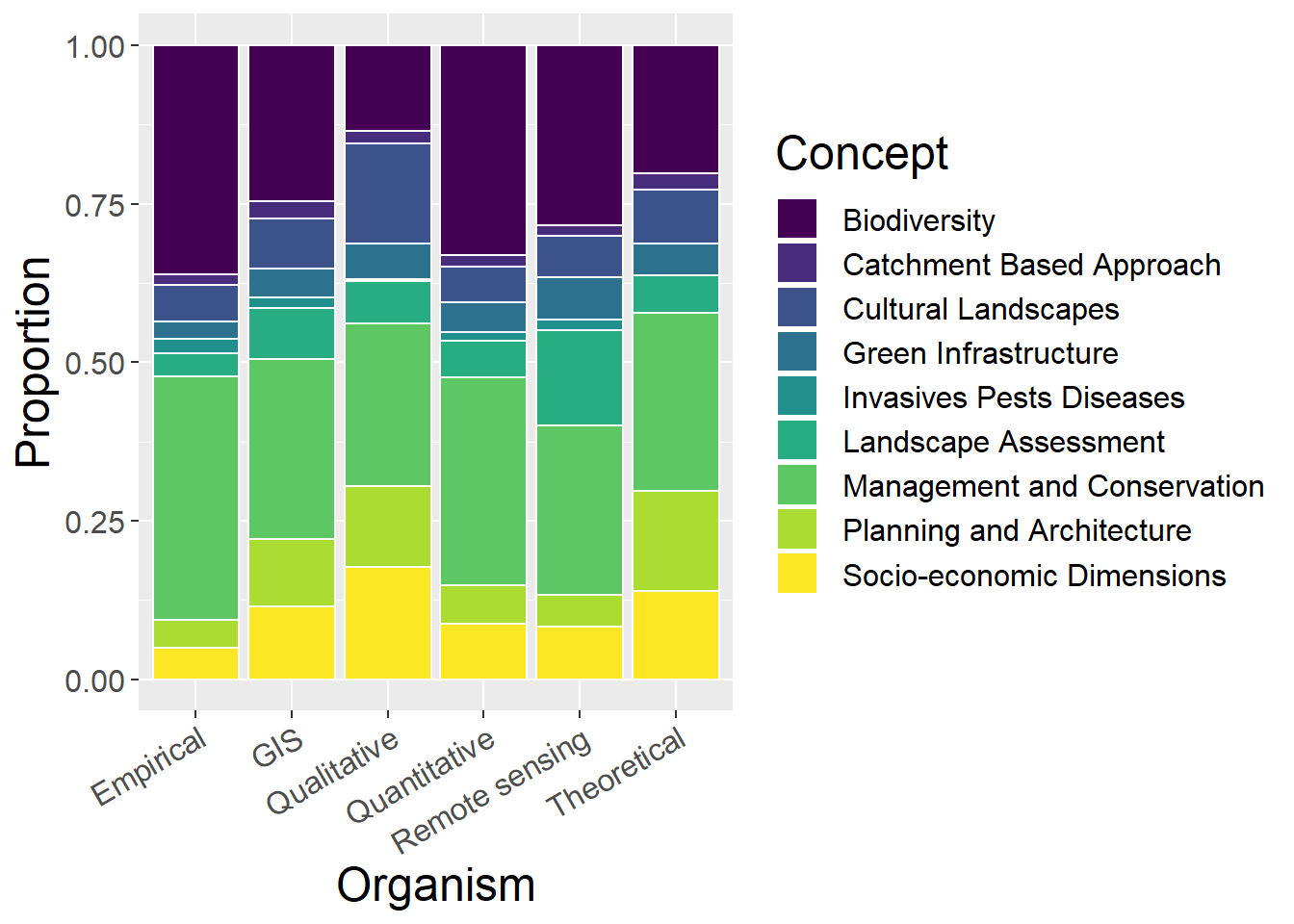
6.8 Other Concepts
General observations:
- Qualitative studies have relatively low proportion of biodiversity studies, but have relatively large proportion of socio-economic and cultural
- Theoretical studies have similar distribution to qualitative slightly more biodiversity at expense of cultural
othCCounts <- metdata %>%
select(Method, `Green Infrastructure`,`Planning and Architecture`,`Management and Conservation`,`Cultural Landscapes`,`Socio-economic Dimensions`,Biodiversity,`Landscape Assessment`,`Catchment Based Approach`,`Invasives Pests Diseases`
) %>%
mutate(sum = rowSums(.[2:10])) %>%
gather(key = Type, value = count, -Method, -sum) %>%
mutate(prop = count / sum)
ggplot(othCCounts, aes(x=Method, y=count, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Concept", y = "Abstract Count", x="Organism")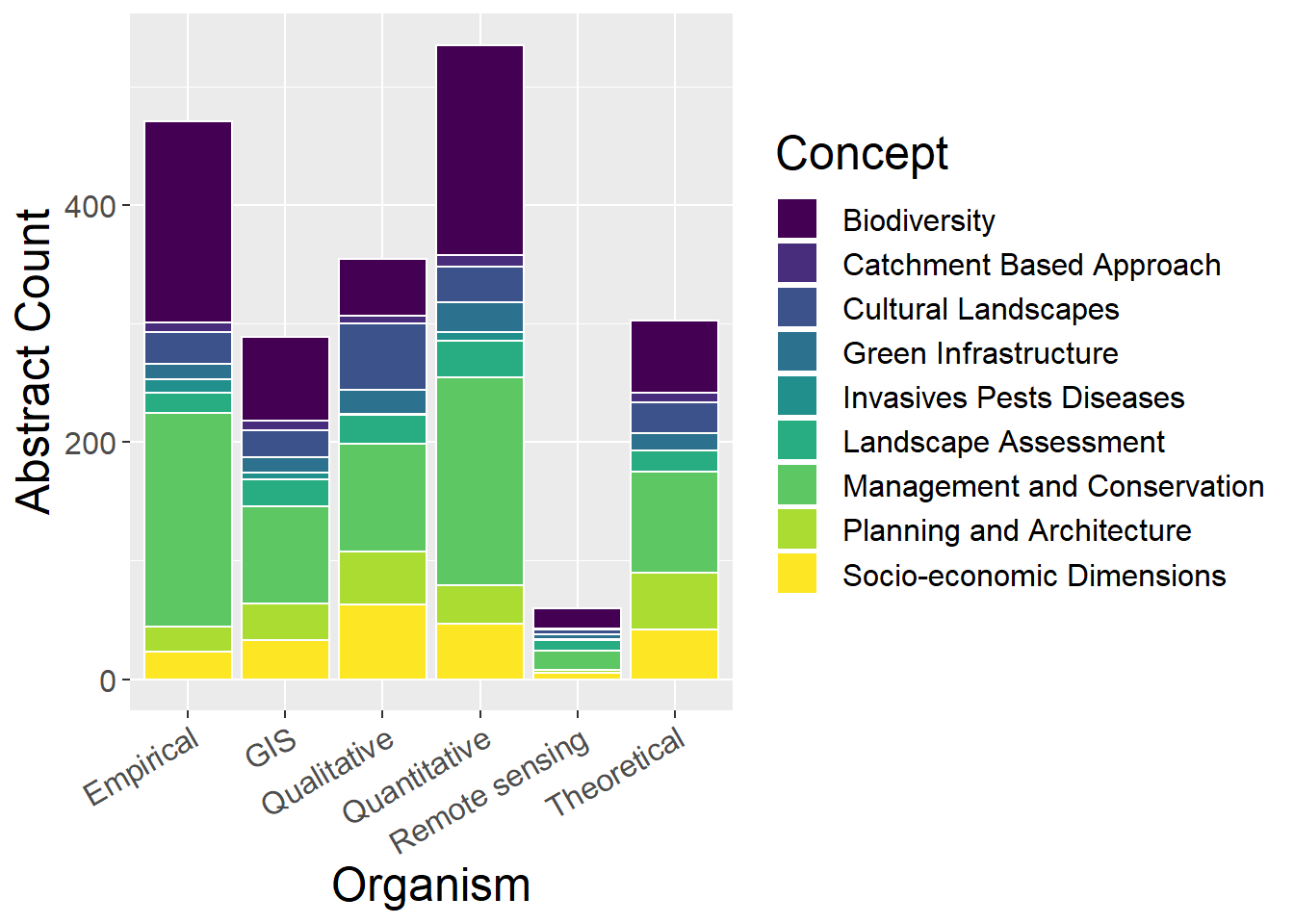
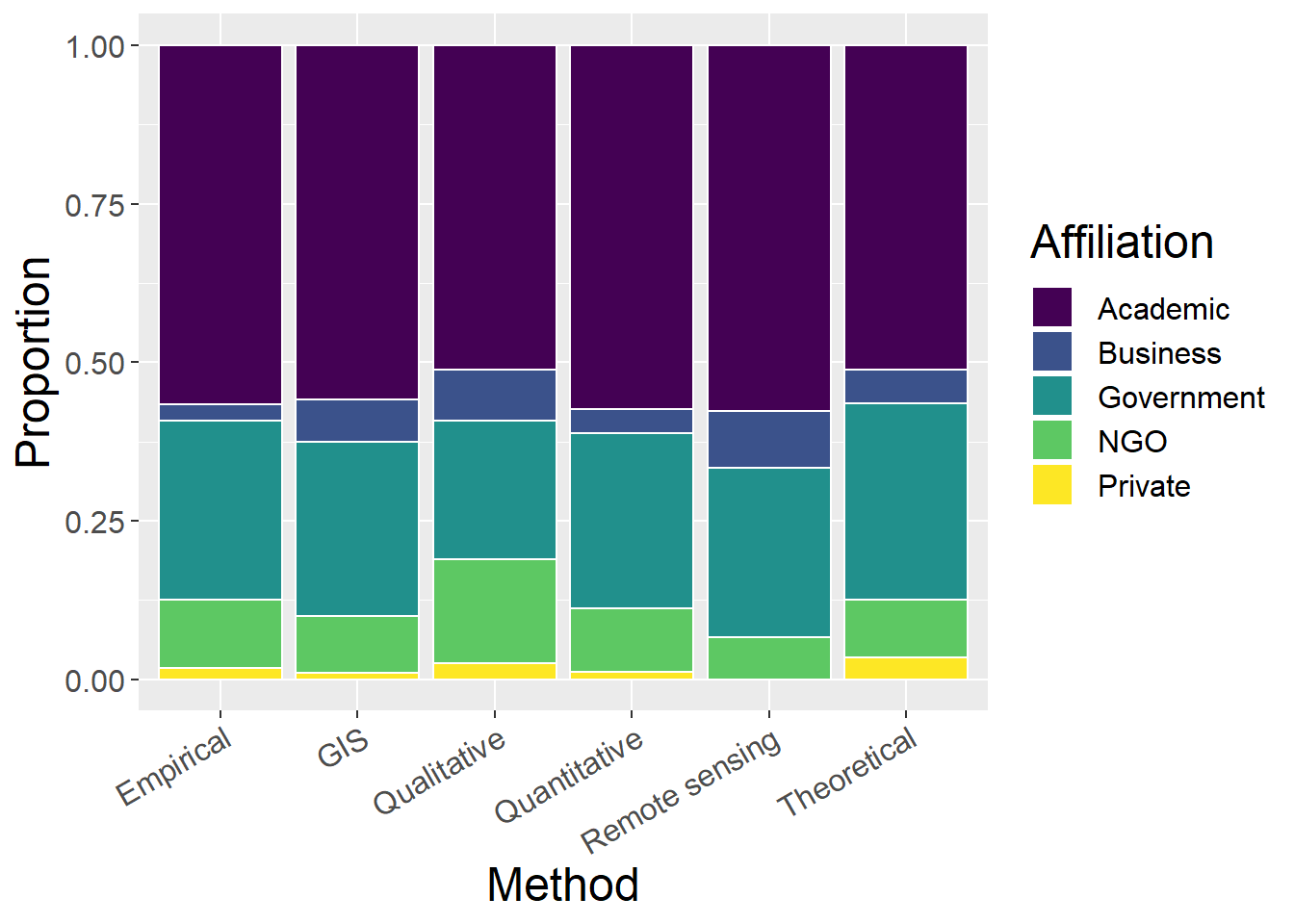
ggplot(othCCounts, aes(x=Method, y=prop, fill=Type)) + geom_bar(stat="identity", colour="white") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = TRUE) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1)) +
labs(fill="Concept", y = "Proportion", x="Organism")